What Is An Isolation Transformer?
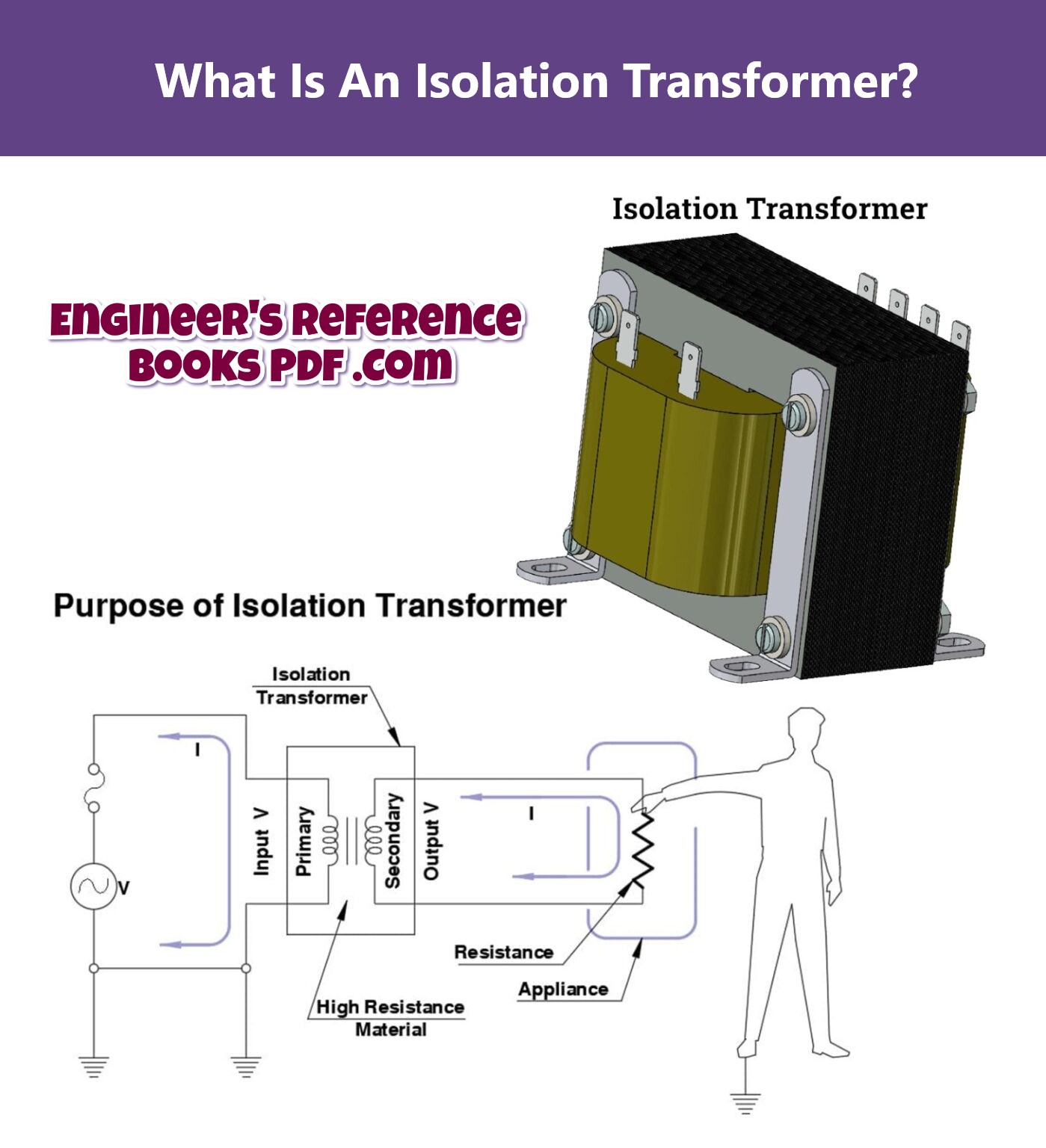
An isolation transformer is a type of transformer that transfers electrical energy from one circuit to another without a direct connection between them.
It is used for safety reasons, to reduce noise and interference, and to isolate various parts of the system.
¹An isolation transformer has two windings: a primary winding and a secondary winding. The primary winding is connected to the power source and the secondary winding is connected to the load.
The windings are wound around a common magnetic core but are electrically separated by an insulating layer.
This prevents direct current (DC) from flowing between the windings and also blocks any noise or common mode transients that might occur on the power line.
¹²The isolation transformer can also vary the level of supply voltage, depending on the number of turns of each winding. If the primary winding has more turns than the secondary winding, the voltage on the secondary winding will be less than the voltage on the primary winding. This is called a step-down transformer.
If the primary winding has fewer turns than the secondary winding, the voltage on the secondary winding is greater than the voltage on the primary winding. This is called a step-up transformer.
Most isolation transformers have the same number of turns in both windings so that the voltage on the secondary winding is equal to the voltage on the primary winding. This is called a 1:1 transformer.
²Some examples of applications where isolation transformers are used are:- Medical equipment: Isolation transformers are used to protect patients and medical staff from electric shock and to prevent interference with other hospital equipment.
²-ElectronicTesting and Services: Isolation transformers are used to isolate test equipment from the device under test and prevent short circuits or ground loops that can damage the device or affect measurements.
¹- Sensitive Equipment: Isolation transformers are used to filter out noise and high-frequency harmonics that can affect the performance or accuracy of computers, laboratory instruments, or audio equipment.
