What is static grounding?
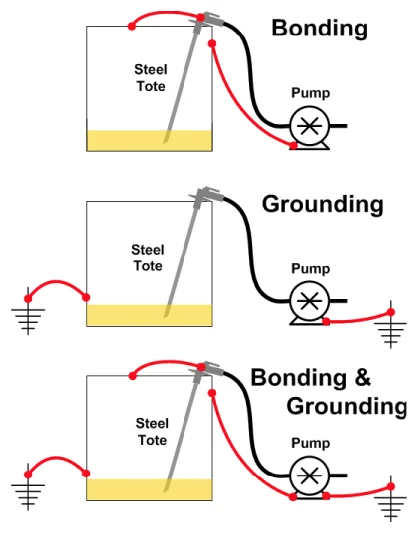
Static grounding eliminates static charge build-up and protects equipment from damage. Static electricity is an imbalance of positive or negative charges between two objects. This charge is generated by the contact and separation (by friction) of two different insulating surfaces. The static charge stays on the object until it sinks to the ground or rapidly loses charge due to discharge.
Grounding
Grounding is a means of discharging accumulated electrical charge. Grounding is the safest way to discharge accumulated static charge. This is done simply by connecting an object to the ground with a ground rod or electrode plugged into the ground. This method of grounding will dissipate static electricity when they are present. This is done by removing excess charge by transferring electrons between the object and the ground.
Airports often have to land statically during the refueling of aircraft.
Aircraft Refueling
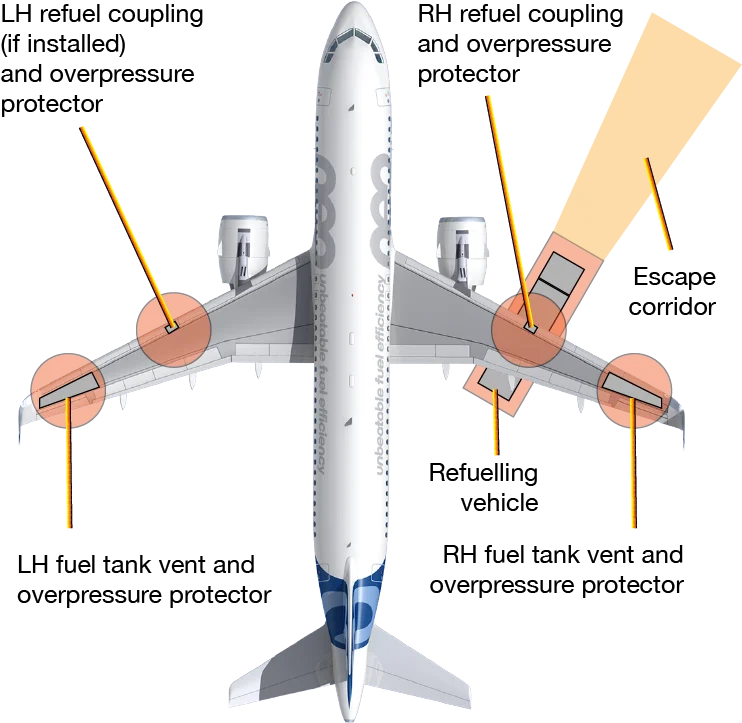

At an airport, the dispenser will provide fuel by connecting the airport’s pressurized fuel pit to the aircraft fuel tank via the filter. Therefore, there are a lot of static charges generated during refueling.
At the airport, a large number of people are near the fuel. In addition, airports are often located in high places, so they are prone to lightning strikes. Static grounding is required whenever the aircraft is refueling. Static grounding is usually achieved by locating a properly installed static grounding on the runway near the refueling area.
Static ground cable shall be connected to the refueling vehicle and aircraft tank before the fuel lines are connected to the aircraft. Static grounding will balance out any potential difference between the two vehicles, which will help prevent static sparks.
Static grounding is usually installed with the completed runway. The socket shall be welded with a ground rod or a ground grid or both. Threaded or cut bar screw sockets are also available. But of these, the threaded connection can increase in strength over time. The static grounding socket comes with a molded ball inside to secure the grounding clamp and is supplied with a cover.
Internal casting balls can also be removable balls. These sockets can be soldered directly to the ground rod. The grounding conductor can be soldered directly to the static grounding plug and at the same time, the plug can be soldered to the ground rod.
Airport structures must be equipped with lightning protection devices. Anchor bars are also commercially available for static grounding and mooring. Installation requires drilling a hole, mounting the assembly, and then filling the hole. In addition, a large washer or steel plates with nuts are required to fix the bar. Sometimes a static grounding/tethering combination is used. This can be soldered to a rod and/or a conductor.
Oil and gas industry

In the oil and gas industry, we need to minimize the risk of ignition due to static electricity. In this industry, static charge can result from the contact and separation of liquids flowing through pipes as well as the process of mixing, pouring, pumping, filtering, or stirring liquids. If there is a gas containing liquid, water vapor, or solid particles such as rust particles or dirt can contribute to a static charge.
Usually, in piping systems, the pipes above the pipe rack have a ground plate welded to the pipe. A distribution grounding plate is equipped with a pipe rack structure and the lines are connected by a grounding cable. The whole system is grounded.