What is electricity and how it is created and used
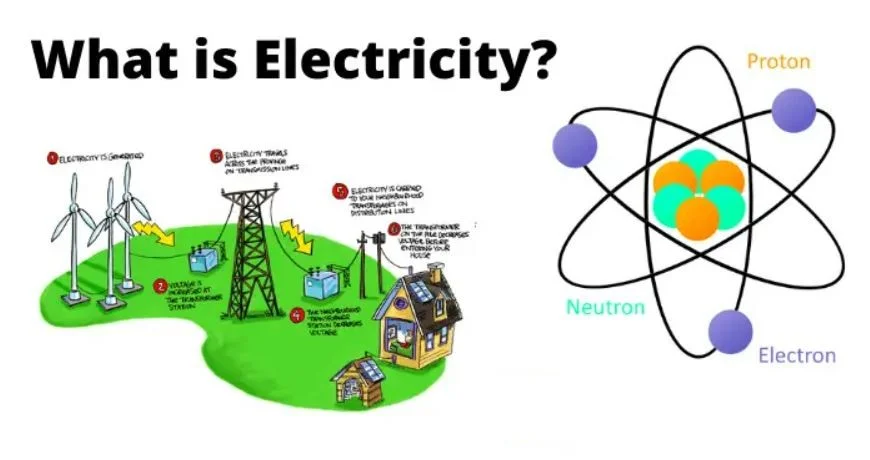
Several inventions have changed human civilization. The first invention was the wheel, the second was electricity, the third was telecommunications and the fourth was the computer. We will discuss the basic birth of electricity. Every substance in this universe is made up of many atoms, and each atom has the same number of negative electrons and a positive number of protons.
Accordingly, we can say that all neutral substances contain the same number of electrons and protons. Protons are immobile and tightly bound to the nucleus of an atom. Electrons are also bound to atoms and orbit the nucleus to varying degrees. But some electrons may be free to move or may be displaced from their orbits due to external influences. These free and weakly bound electrons cause electricity.
In the neutral state, the number of electrons and protons in any substance is the same. But if somehow the number of electrons in a substance becomes greater than the number of protons, the substance becomes negatively charged because the net charge of each electron is negative. If the number of electrons in a substance becomes less than the number of protons, the substance becomes positively charged.
The concentration of free electrons is always the same. This is the sole reason for electricity. Let us explain in detail. If two conductors of different signs are in contact, electrons from the one with the higher electron concentration will move to the one with the lower electron concentration to balance the electron concentrations of the two objects. This movement of charge (since electrons are charged particles) is electrical.
Electrical terms
Charge: As noted above, the number of electrons and the number of protons is equal in a neutral object. The amount of negative charge and positive change is also equal in a neutral object because the charges of electrons and protons are equal in number but their polarities are opposite. But for some reason, the balance of the number of electrons and protons in a body is distributed, and that body becomes charged. If the number of electrons is more than the number of protons, the
body will become negatively charged and the amount of charge depends on the excess number of electrons in the body. In a similar way, we can explain the positive change of an organism. Here, the number of electrons becomes less than the number of protons. Body positivity depends on the difference between protons and electrons in the body.
Current: When a charge flows from one point to another to evenly distribute the charge, the rate at which the charge flows is called current. This speed mainly depends on the difference between the charged states of the two points and the conditions of the line through which the charge flows. The unit of currency is the ampere and it is nothing but the coulomb per second.
Electric potential: The degree of the electrical charge of an object called electric potential. When a body is charged, it will be able to do a certain job. Electric potential is a measure of a charged object’s ability to do work. The amount of current flowing through a conductor is directly proportional to the potential difference between the two conductors. Electrical potential can be visualized as the difference in water level in two water tanks connected to a pipe. The speed of water flowing from the upper head tank to the lower head tank depends on the difference in water level or head of the water in the tanks, not on the amount of water contained in the tanks. Likewise, the current between two objects depends on the potential difference between the two objects, not on the amount of charge stored in the objects.
Electric field: Between two charged objects placed close together, there is always an interaction force. The force can be attractive or repulsive depending on the nature of the charge of the two bodies. When a charged body enters the vicinity of another charged body, the actual force is felt. The space surrounding a charged body where another charged object can experience a force called the electric field of the first.
The four terms mentioned above are the main electrical parameters.
How to generate electricity
There are three basic ways we generate electricity.
Electromechanical process: When a conductor moves in a magnetic field and the conductor passes through the magnetic field lines, an electric current is generated in the conductor. According to this principle, all generators work as d.c. generators, a.c. generators, and all types of generators. Electrochemical process: In all batteries, electricity is generated by chemical reactions. Here, chemical energy is converted into electrical energy.
Solid State Power Generation: This is the most modern power generation process. Here, free electrons and holes are generated at a PN junction and the distribution of charge carriers is unbalanced across the PN junction when the junction is exposed to light. These free electrons and holes and their unbalanced distribution across the junction cause current in the external circuit. According to this principle, PV solar cells work.
Types of Electricity
When electricity is generated in the armature of a generator, it is always alternating. This means that the polarity of the electricity changes over a periodic period of time. In a DC generator, the electricity generated in the armature is rectified by the commutator. In an AC generator, the alternating current generated in the armature feeds the external circuit through slip rings.
When the current does not change direction, it is called direct current. Batteries and solar cells generate direct currents.
Electricity generation Electricity transmission and distribution
What is electricity, and how it is generated and used

Electricity, once generated in a power plant, is boosted by a transformer booster for transmission purposes. Low-voltage power generation is convenient and economic. But low voltage transmission is uneconomical. But for power transmission, the generated electricity is first increased, and then after transmission, it is reduced by step-down transformers for the purpose of power distribution. Power generation, transmission, and normal electricity distribution by the 3-phase system. The transmission of extremely high voltage alternating current is not always economical and that is why DC transmission is sometimes used. The electrical system in homes may be single-phase AC, but all power in commercial, industrial, and larger homes is three-phase.






