Difference between brazing and brazing

One of the many techniques used to join two or many metal pieces is brazing and brazing. Metal washers are made by hot bonding two or more metal alloys together. In this case, gluing is more than simply attaching the elements together, as the joint will be molecularly bonded to the alloy, increasing its strength.
Only tin solder and tin solder are capable of producing contours on the edges of smooth and shaped metal joints. In both processes, the joint surfaces and filler metal are heated above room temperature.
The only real difference between the two methods of joining metal is the temperature at which they are performed. Unlike the weld filler metals which melt below 450°C, the weld filler metals melt above this temperature. Here we will discuss them in more detail.
What is tin solder?
Fusing two or more metal parts by heating them to a temperature above their melting point but below the melting point of the base metal is called tin soldering. Next, the solder alloy or filler metal is heated and melted.
Thanks to capillary action, it flows into the junction where two metal parts meet. This process is commonly used for materials including metals, ceramics, glass, plastics, and composite materials.
This metal bonding method is stronger than fusion welding but does not melt the base metal of the parts to be joined. Therefore, this process requires more heat input than other welding operations such as mechanical fastening, bonding, solid-state splicing, soldering, etc.
It is commonly used in plumbing and metalworking applications, as well as in the aerospace, automotive, and HVAC (heating, ventilation, and air-conditioning) manufacturing sectors.
Compared with other joining techniques such as brazing, brazing has more advantages. In addition to combining different metals with different melting points, it can produce a strong, tight weld and a neat, attractive finish. If necessary, the solder joints can also be easily disassembled without damaging the individual components.
Advantages of Welding
This process requires less energy and heat.
This process can combine different metals, including metals with different melting points. Welding
is a quick and affordable process for bulk production as it can be automated.
It allows the assembly of fragile or fragile parts that other assembly processes could fail.
To increase part life and reduce waste, welding can be used to repair worn or damaged parts.
Welding Disadvantages
Welds are less durable, making them potentially unsuitable for high-stress applications.
The risk of uneven heat distribution makes it unsuitable for joining thick metal parts.
Since copper welding requires a certain level of expertise and experience to produce good results, labor and training costs can increase.
Some gaskets may not be suitable, especially those with complex shapes or tight tolerances.
Due to the cost of filler metal and the need for specialized equipment, welding can be more expensive than other joining methods.
What is welding?
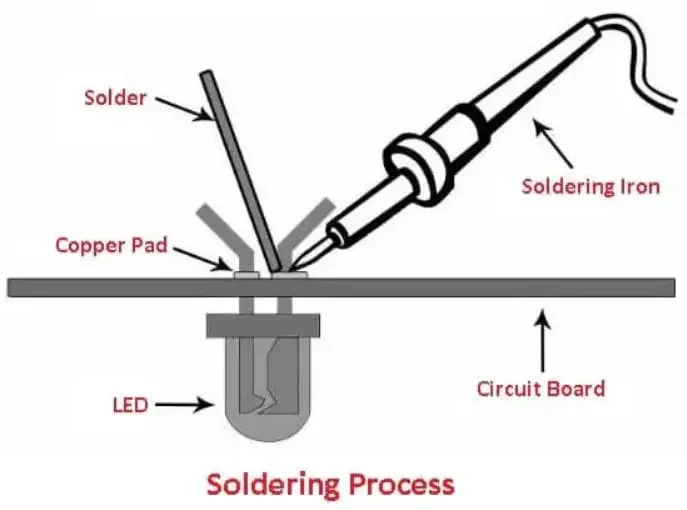
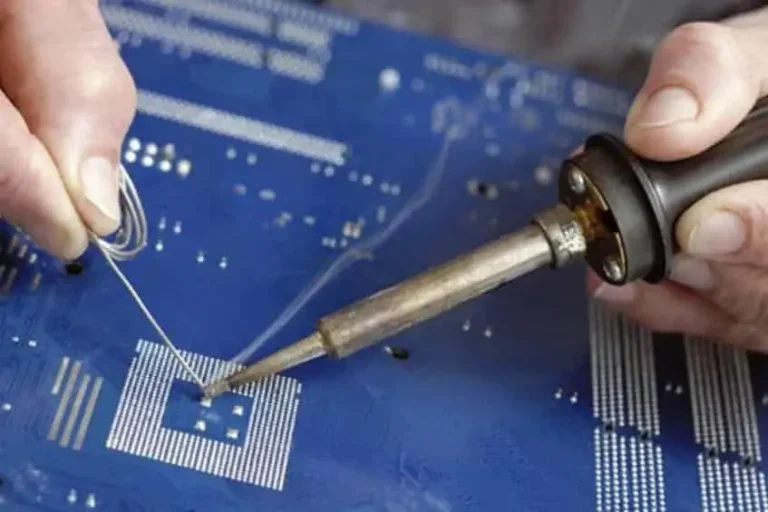
When two or more metal parts are heated to a temperature where the filler metal known as solder melts and flows through the joint, creating a strong electrical and mechanical connection, the process is called weld.
The soldering iron melts the filler metal (the solder) at low temperatures up to 450°C. Because the filler metals melt at low temperatures, heat damage to delicate parts and warping of parts are minimized. As the solder solidifies, it bonds to the metal parts to join them together.
Lead-tin alloy solder is the most common. In the electronics industry, soldering is widely used to connect wires, capacitors, resistors, and other components to the junction plate. It is also applied in plumbing, jewelry making, and other metalworking processes.
Welding is slightly different from soldering, which involves melting the base metal to create a fusion. Welding is often chosen for its adaptability to various metals and its suitability for delicate work.
Advantages of Solder
For use in electronic circuits, solder creates a strong and reliable bond between metal components. Solder.
is suitable for fragile or heat-sensitive materials because it uses lower temperatures.
Various metals, wires, and light parts can all be joined by soldering.
Welding is a fast and efficient, economical process for mass production.
Welding is a safer choice than other types of metal joining processes because it produces no radiation.
Disadvantages of Welding
The strength of the weld is usually lower than that of other types of joints.
Beginners may have difficulty welding as it requires specific levels of training, knowledge, and equipment.
Due to the low melting point of the solder, high-temperature welding is not recommended.
Can’t weld on heavy metal.
Improper heating can lead to gaps or distortions in the weld.
Difference between copper soldering and soldering
While two or more metal parts can be joined by copper soldering and brazing, there are significant differences between the two processes.
The main differences between brazing and brazing are as follows:
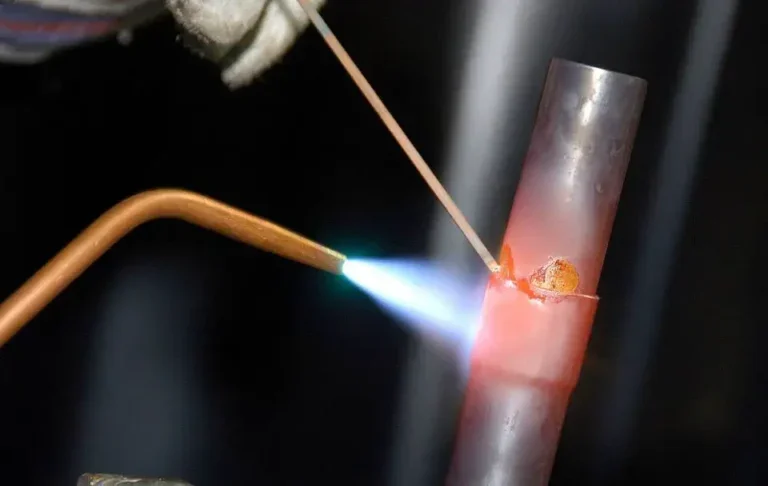
#1 Terminology
The terms brazing and brazing are methods of joining the same or dissimilar metals, but they are used in a variety of assembly working conditions.
During welding, a metal filler is melted and poured into the joint used to join two pieces of metal. When welding, a filler metal called solder is also used to fill the joint, creating an alloy on the metal surface without melting the base metal.
#2 Temperature
The temperature used for brazing is similar to the melting point used for soldering. The main difference between these two metal joining techniques is the temperature at which they are performed.
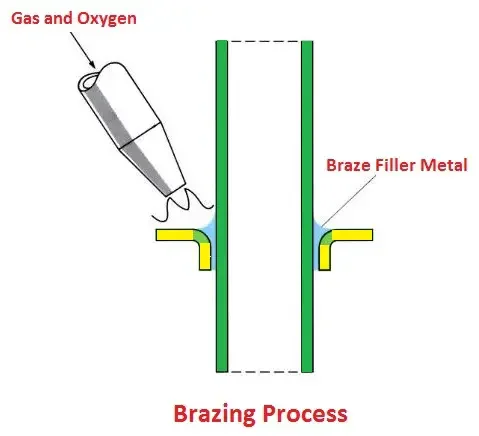
The brazing process involves heating the filler metal to a temperature above 450°C (840°F). The welding process, on the other hand, uses filler alloys with a melting point below 450°C (840°F).
#3 Strength
Brazed joints tend to be more durable than welded joints. Due to the higher temperature of the welding process, the filler metal and the components to be joined can form a stronger metallurgical bond.
#4 Gap
Welding requires a smaller clearance between the metal parts to be joined than welding, which requires a larger clearance. This is because the welding process requires higher temperatures, which can cause metal components to expand and contract. As a result, there must be a wider opening to allow movement.
#5 Surface preparation
Brazing generally requires more surface preparation than brazing. To enhance the strong adhesion of filler metal, the metal surfaces to be joined must be cleaned and roughened.
#6 Cost
Copper soldering is generally more expensive than copper soldering because the higher temperatures, specialized equipment, and materials required for welding make the process more expensive.
#7 Applications
In the electronics industry, soldering is the most frequently used process to create durable connections between electronic components. It is commonly used in plumbing, electronics, crafts, engine repair, and metalworking, from jewelry to flashes. The soldering technique connects wires to wires on switches and other components.
Flux is used in welding to aid in the wetting and removal of oxides from the base material. This improves the bond between the filler metal and the metal components. With the exception of aluminum and magnesium, all metals are usually joined together by welding. Also, car manufacturers use it.
Welding vs Welding: Which is better?
Depending on the application and specific requirements, copper soldering or soldering should be used. The choice between copper and electric welding will depend on a number of factors, including the metals being joined, required strength, temperature, and environment, as well as budget and time constraints on the project.
Applications such as aerospace and automotive manufacturing, which require very strong joints, high-temperature resistance, and good mechanical properties, are generally preferable to welding. Soldering is more expensive and takes longer than soldering. Since it requires higher temperatures, precise clearances between components, and specialized equipment.
Solder is generally preferred for applications that require lower temperatures, low resistance joints, and greater flexibility, such as electronics, jewelry, and plumbing. Compared to copper welding, copper welding is simpler, faster, and can join a wider range of materials, including fragile parts and metals of different alloys.
So brazing or tin soldering is equally valuable – the best choice is based on the specific application and requirements.