Types of Underground Cables
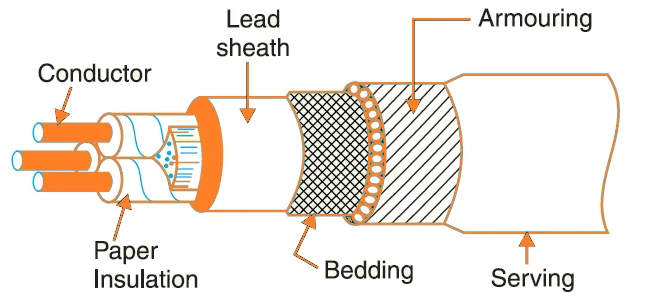
This article describes the types of submarine cables. Underground cables are used to transport electricity from the power plant to the distribution station. Unlike overhead power lines, these cables are laid underground in locations where it is impractical, difficult, or dangerous to use overhead power lines. They are mainly used in densely populated areas, and the initial cost is higher than overhead power lines of the same capacity.
Types of Underground Cables
Underground cables are of different types and can be classified into different groups. Underground Cables May be Classed Based on
Rated Voltage
Number of Conductors in Cable
Insulation Type
Cable Construction
Installation
Types of Underground Cable Based on Rated Voltage
Types of Underground Cables
The system voltage at which the cable is intended to operate is an important criterion for classifying these cables. Insulation level, current carrying capacity, impedance, etc. determined according to the rated voltage.
There are different types of cables that operate at different voltages, such as
Low voltage cables: These cables operate at voltages up to 1kV.
High voltage cable: Operating voltage up to 11kV.
Super voltage cable: Operating voltage up to 33kV.
Very high voltage cable: Operating voltage up to 66kV.
Extra voltage super cable: Working voltage over 132kV.
Higher voltage cables are used in power transmission because the generated voltage is increased to a higher value in order to reduce the current to transmit a certain amount of power. The higher the voltage rating, the thinner the cable will be, reducing weight, installation costs, and impedance.
Underground cables based on the number of conductors
This classification is based on the following criteria
The expected load the cable will carry
Voltage drop in the cable
Rated continuous current of the cable
Ground fault loop impedance
So there are different types of cables like-
3-core cables: These cables are used for perfectly balanced three-phase systems. A perfectly balanced three-phase system is one in which the three-phase currents are of equal magnitude and deviate from each other by an angle of exactly 120 degrees. These cables do not have a neutral because the three-phase loads are identical.
3.5 Conductor cables: These cables have a neutral conductor allowing the cable to be used at higher voltages. Such a system may not have identical loads and thus the neutral helps to carry the unbalanced current. The higher the unbalance, the greater the neutral current will be.
4-conductor cables: These cables are used when the unbalanced currents are very high and the loads are not linear. Non-linear loads like SMPS, electronic ballasts, electronic dimmers, etc. produce a third harmonic current in phase with all supply phases. These third harmonic currents do not cancel out as in the case of a balanced system, but they add up. As a result, the neutral is subjected to very high unbalanced currents. These neutral wires have the same
thickness as the main conductor because they carry very large currents.
5 and 6 conductor cables: Used in systems where unbalanced or neutral currents can become very large relative to phase currents.
Cables with 3 or 4 conductors are commonly used in the case of underground cables.

Types of Underground Cables
Types of Cables Based on Insulation Type
The insulation of an underground cable plays an important role in its classification. The insulation ensures the safety of the internal conductors against the elements as well as their safe handling. The degree of insulation required depends on the system voltage and the operating temperature.
Various materials such as paper, rubber, PVC, cross-linked polyethylene, etc. are used as insulating materials. They are selected according to their respective dielectric strength. Below are some insulating materials and their respective dielectric strengths.
Insulating material Dielectric strength
PVC 200kV/cm
Mica 118MV/m
Teflon 60MV/m
Glass 14MV/m
Rubber 12MV/m
Impregnated paper 30kV/mm
Silicone insulator 20MV/ m
HDPE Insulator 20MV/m
Nylon 14MV/m
Porcelain Insulator 12MV/m
Air 3MV/m
Vacuum 30MV/m
It should be noted that actual ratings may vary due to factors different operating factors.
Underground cables based on the construction
Underground cables can be classified according to their respective construction. This is
1. belt cables
In these cables, there are usually three conductors grouped together and held together by a paper belt. Each cable conductor is insulated by impregnated paper insulation. The space between the conductors and the insulating paper belt is filled with fibrous material such as jute, which gives the cable flexibility as well as its round shape. This jute layer is then protected with a metal sheath and weave. Such cables do not have a perfectly round shape. This is done to make efficient use of the
space available in the cable.
2. Shielded cable
Shielded cable is available in two types – class H and class S.L.
H-Type
In class H cables, the individual conductors are first insulated with insulating paper, followed by a metal sheath. These metal caps are thus in contact with each other, which are then grouped together by a metal band that usually includes a cap. Finally, a lead sheath is provided around and the lead sheath and copper tape are grounded.
S.L.Category
It is similar to a Category H cable except that individual lead sheath are provided for each conductor instead of the overall sheath. The advantage is that the risk of conductor-to-conductor damage is reduced and the cable increases flexibility.
H.S.L Type
These cables are a combination of H and S. Category L cables. Each core is insulated with insulating paper and is provided with a separate lead sheath.
Pressure cables
For system voltages above 66 kV, the electrostatic force acting on the cable is very severe. This can lead to insulation failure and permanent cable damage. To avoid this, pressure cables filled with oil or gas are used instead of solid cables to improve dielectric strength.
Oil Filled Cables
Oil is filled through the cable under proper pressure. This oil is used for impregnating the insulating paper.
Gas Filled Cables
Pressurized gas flows around the cables in a steel tube.
Normally the gas is nitrogen. Such cables are used in high voltage transmission and high load current.
Underground cables based on installation
Direct burial installation: A trench is dug and the cable is placed in it without any additional components. A cooling tube can be provided if required.
Installation of tunnels: Tunnels are dug where electrical cables must cross the river. The cables are laid in the tunnel. However, the installation and maintenance costs are high.
Piping Installation: Concrete conduits are dug and cables laid. Maintenance is easy and accessible as they are visible on the ground.
Gas-insulated line installation: For power lines operating at very high voltages, gas insulation is provided during installation. It provides operational safety but the initial cost is high. This is a relatively new technique for installing electrical cables.